The Internet is an inseparable part to us humans. Enabling us to access an enormous amount of information from a device we hold in our hand. Access to information is instant!. Physical part of the internet one may see is a Wi-Fi modem with its blinking lights, lying around in the corner, cables running from the modem to outside your home. Where does that cable go?
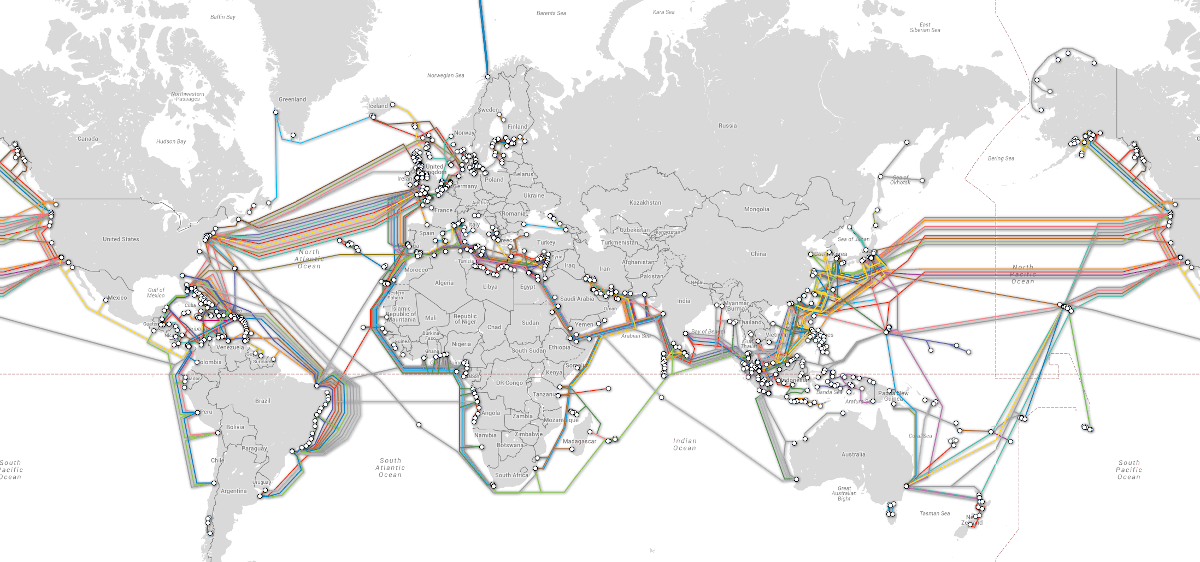
“The internet’s” physical infrastructure is huge and numerous. With large networks of fiber which sends and receives data in form of light(laser), Huge refrigerator size routers(called core), Internet exchanges, fibers connecting continents, data centers where the data destined to become stationary or the cloud; fancy way to say “stored on someone else computer”.
Services that require high bandwidth and low latency are emerging and becoming part of one’s logical world. Let’s assume, Everyone stops using cable boxes and starts using streaming services, which is already happening. If the streaming service servers are outside India, then the stress would be felt on undersea cable. Increasing the capacity of intercontinental fiber requires time and money. This makes business/financial sense for companies to move their infrastructure locally, closer to their customers. We have seen google, Facebook, Netflix and more setting up their data centers in our country, Using CDNS, ISP’s and Internet Exchanges peering and promoting to make data access stable, fast and less expensive. Logical part grows so does the physical part.
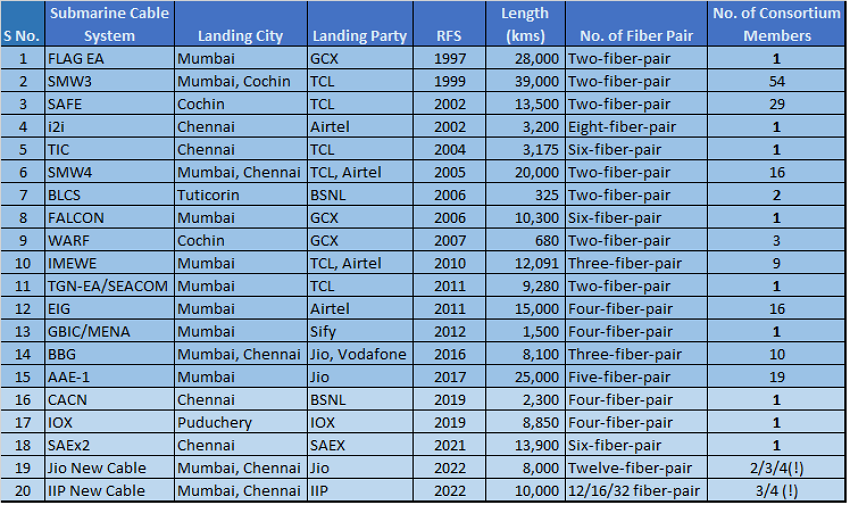
Undersea cables, which is connects us to rest of the world. Their landing stations located at Kochi, Trivandrum, Mumbai, Chennai, Pondicherry and Tuticorin. Main player(tier1) who own these cables are, TATA(The biggest player in India’s internet space, and emerging major in global space), Airtel, Reliance Jio, BSNL, Sify, Vodafone, Global Cloud Exchange, IOX. Combined Speed of these links goes up many Tbps with bandwidth to spare.
List Of Cable
Governments are bringing more and more citizens to the logical world. In India, the number of internet users stands around 56 Cr. Kerala(state in southern tip of India), State’s High Court gave a verdict few years back that “right to have access to the internet is part of the fundamental Right to Education as well as the Right to Privacy under Article 21 of the Constitution of India”. State’s population stands around 3.5cr, and 56% of state population has internet access.
State of Kerala, where I am from, a small state but a beautiful one, with its lush green mountains, backwaters, beaches and most importantly the great people who inhabit these lands.
The Government of Kerala hopefully has been going by the court judgement as baseline, is making great strides in connecting the whole of Kerala household to the internet. Creating states own fiber network named Kerala Fiber Optic Network(KFON). Impact of this would be seen in coming decades.
When writing about the internet should mention little of history, when the revolution started. The ARPANET(USA military project) and the IMP’s(Educational project which is first inter network). How it has evolved to huge fiber infrastructure sending data with lights. All the underwater cables connecting continents. Openness and its humongous physical infrastructures strategically placed around the world sucking up 4% of global energy produced.
For historical context, ARPANET was christened in 1969. Then the IMP’S that connected universities same year. IMP(Interface Message Processor) can be said to be the beginning of the internet revolution.
17 years later India had its ERNET(1986). By that time TCP/IP and OSI was already standardized and as we know TCP/IP prevailed. Huge problems were encountered in the early stages of the public internet in India. ERNET connected educational institutions; IIT’S. Later NICNet(1995) to connect government institutions.
In 1995 VSNL launched the internet service to the public on auspicious day of August 15, 1995. VSNL used dial up protocol SLIP/PPP a speed of 9.6 kbit/s speed and was priced at 5000Rs for 250 hours for individuals, costly in those time money.
Now here we are in 2020, how things have changed!
GiBu GeorGe